You may have a problem with your baseboard heater and believe the fuse is to blame, which is why you came to this page. Trying to look for an answer to where your baseboard heater's fuse is located. To give you the solution, we did in-depth research.
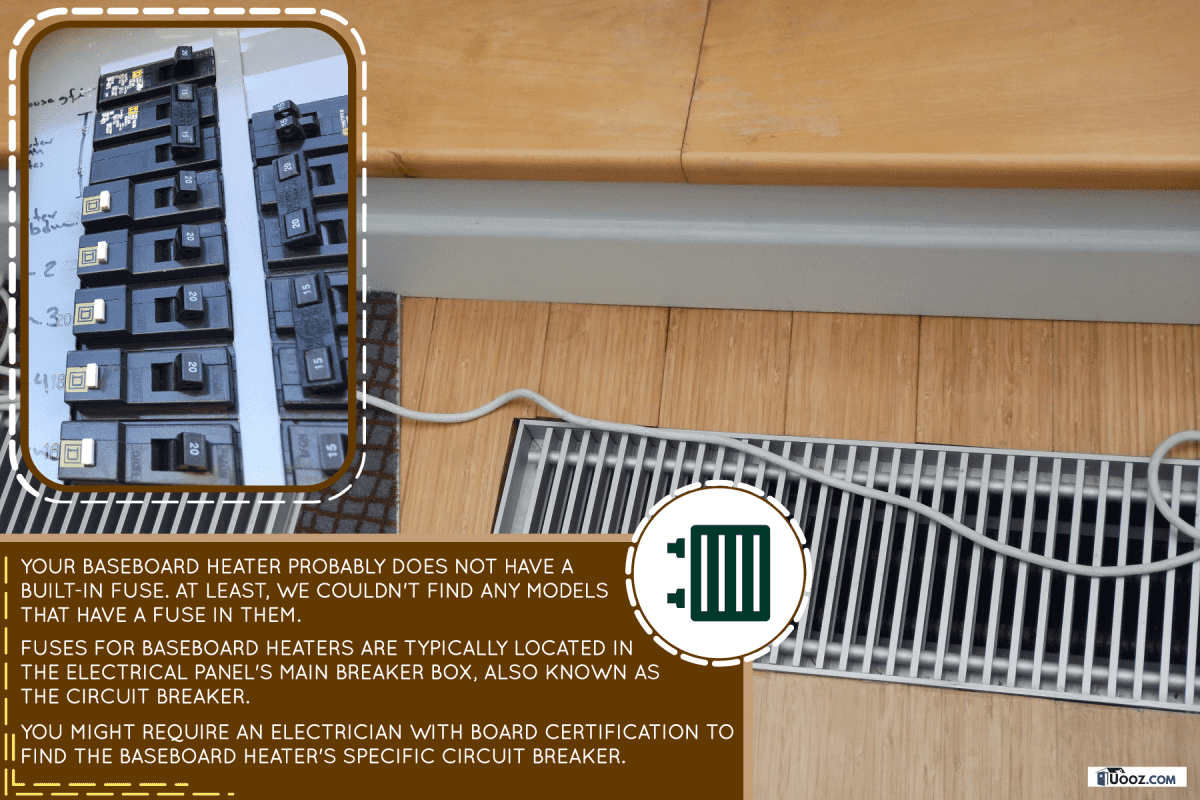
Your baseboard heater probably does not have a built-in fuse. At least, we couldn't find any models that have a fuse in them.
Fuses for baseboard heaters are typically located in the electrical panel's main breaker box, also known as the circuit breaker.
You might require an electrician with board certification to find the baseboard heater's specific circuit breaker.
One of a home's essential needs is baseboard heaters. Using baseboard heaters is a practical and affordable solution to offset the heat loss from window glass. But if not properly treated, baseboard heaters can occasionally experience issues.
Now that you know the fuse's location, you might wonder how to verify a suitable fuse and what causes a fuse to explode. To learn more, read this article through to the bottom.
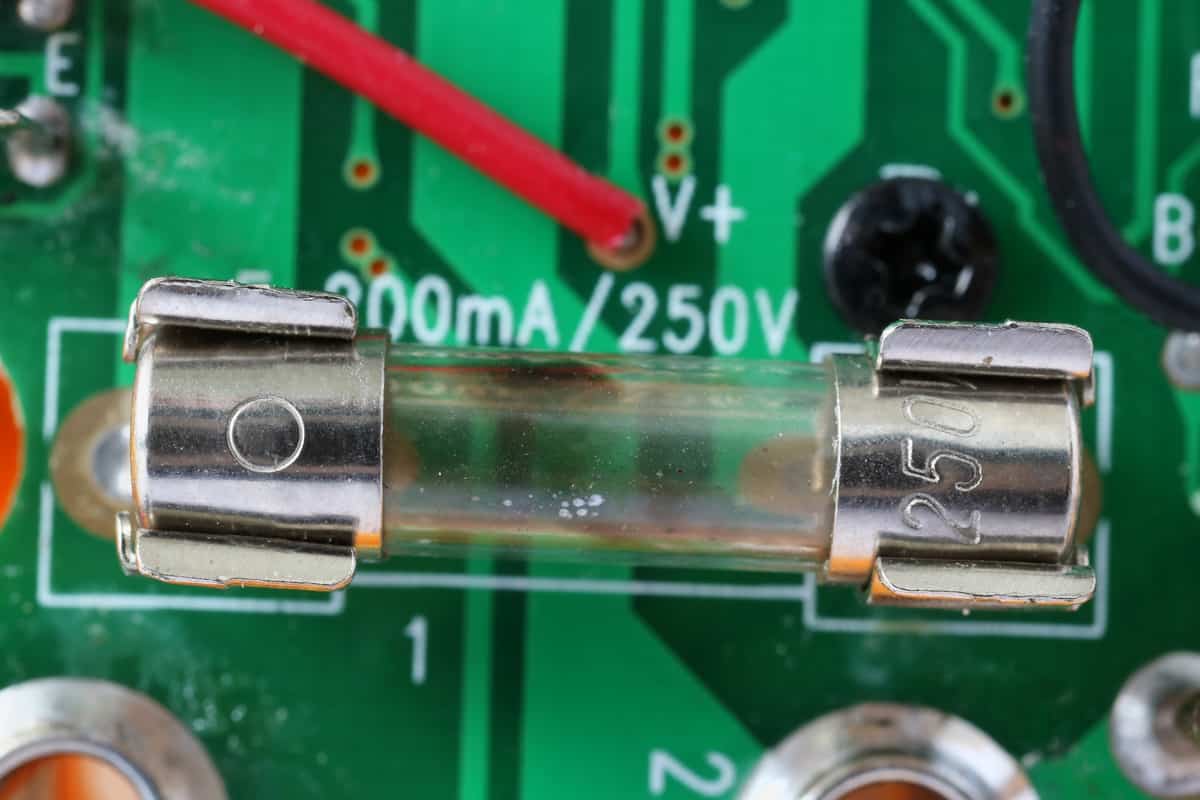
Inspecting for a Blown Fuse: A Guide
Check out the glass fuses-holding containers by opening the fuse box. Examine every fuse in detail. A functional fuse's glass container will be visible.
If a fuse blows, the glass container may be gray-black or grey or have metal debris on the sides, cutting off the electricity to the circuit to safeguard it.
Use a multimeter to determine if the fuse has blown if you cannot see it. The multimeter's resistance, or Ohms setting, should be selected on a multimeter.
Connect the multimeter's first lead to one end of the fuse and the second lead
to the opposite end. The fuse is okay if the reading falls within the range of 0 and 5 Ohms.
A higher value indicates a damaged or deteriorated fuse. A blown a fuse is unmistakably shown by the reading OL (Over Limit).

This sample video teaches how to use a multimeter to check fuses.
Find this multimeter on Amazon.
Causes of Blown Fuses
The circuit breaker may be set off by a blown a fuse, which will turn off the electricity to a particular area of your home. Finding the source of the issue will assist you in quickly turning the power back on.

If determining the reason for a blown a fuse seems difficult, continue reading to learn the possible causes.
Short Circuit
A breaker trip can have more significant causes, such as a short circuit. When the black hot wire makes contact with the white neutral wire, the exposed bond or ground wire, or the metal box's case, it results in a hard short.
According to physics, a short circuit reduces resistance, allowing electricity to flow unhindered suddenly, and this sudden rise in current flow inside the breaker triggers the tripping mechanism.
However, occasionally a short circuit happens not at all because of the wiring of the circuit but rather due to a wiring issue in a device or appliance connected to such an outlet and along the circuit.
Circuit Overload
The most frequent cause of a circuit breaker failure is an overloaded electrical circuit. It happens when a circuit tries to draw more electricity than it can handle.
The circuit breaker's internal detecting mechanism heats up when a large number of appliances or light fixtures are functioning at once, and the breaker trips—typically via a spring-loaded element inside the breaker—when this happens.
As a result, the circuit becomes inactive, and the breaker's continuous passage is broken. The internal spring mechanism is not re-armed until the breaker lever is returned to the ON position, which also turns on the circuit.
The capacity of the wires in this circuit is reflected in the size of the circuit breaker or fuse. As a result, the breaker or fuse is designed to trip or blow even before the circuit wires get dangerously hot.
If a circuit breaker routinely trips or a fuse frequently blows, you should move some appliances and equipment to other circuits. This indicates that the course is loaded beyond capacity.
Alternatively, it can indicate that your home needs more service because there aren't enough circuits. When a circuit is overloaded, the breaker normally takes 10 seconds to trip due to a time delay mechanism incorporated into the device.

Fault Arc
A unique kind of circuit breaker described as an arc-fault circuit interrupter, or AFCI has seen its specifications significantly expanded in recent times. This is according to the National Electrical Code, on which the vast majority of regional electrical codes are based.
Aside from tripping in response to short circuits, grounding faults, and overloads, AFCI breakers may also detect voltage instability. This is brought on by sparking points of contact inside a wire connection.
For instance, unsecured screw terminal contacts in such an outlet or switch may be the source of this. Therefore, an AFCI breaker detects early electrical issues before they could result in faulty wiring or ground faults.
Regular circuit breakers and fuses provide no defense against arc problems. A crucial defense against arcing-related fires is arc fault protection.
The same process is used to reset AFCI breakers for standard breakers. As a result of repeated arcing caused by loose wire connections anywhere along the circuit, recurrent tripping is typically a symptom of this.
Ground Fault
A ground fault, a particular type of short circuit, occurs when a hot wire makes contact with a ground wire, a metal wall box, or metal framing members.
Ground faults can be very dangerous. This is especially if they happen outside or in moist areas like bathrooms or kitchens. When a ground fault occurs, there is a known danger of shock.
There are steps you can take to identify and fix a ground fault. However, you must also take important ones to prevent one from occurring in the first place.
For instance, some regulations may require that outlets be protected with GFCIs in places where direct contact with the ground or water is possible.
Similar to hard shorts, a ground fault causes an instantaneous decrease in resistance and an instantaneous increase in electrical flow.
The internal mechanism of the circuit breaker overheats, as a result, tripping it. If a ground fault is found, just like with hard shorts, the circuit breaker could trip again soon away after you reset it.
Blown Fuse Replacement
To start with, find the fuse box. The typical appearance is that of a front-doored rectangular metal box. Typically, fuse boxes are located in a basement or garage next to the electric meter.
If your property has a screw-in fuse board, it must be replaced by an electrician because they are no longer functioning and cannot be replaced.
Find out the specific circuit the blown fuse has affected. To find the location where the power is out, start by walking around your house and turning on and off each light.
Lights should be turned off. Also, all electrically powered furniture, equipment, and devices should be disconnected before attempting to fix a blown fuse.

Your home's main switch should be turned off. You can then detach the blown fuse by standing just on the rubber mat located in front of the fuse box after you've completed this.
To avoid an accident that could result in burns or an electric shock, be careful not to contact the metal threads as you remove the fuse.
Determine the fuse's amperage rating by looking at it. The rating is generally engraved on the steel button of the fuse base, printed on a label affixed to the fuse, or molded into the glass container.
Using a replacement fuse that has the identical amperage rating as that of the blown one. You should replace the damaged fuse. Insert the new fuse into the socket where the old fuse was.
At the main switch, turn on the electricity. The circuit ought to get back to functioning. Put the rubber mat aside and close the fuse box.
Wrap Up

Despite the possibility of a fire, baseboard heaters are effective in heating homes. To safeguard your home from the risks of an electrical system that isn't functioning properly, make sure you are aware of where to check for fuses, how to examine them, and when to repair them.
You may also hire a specialist to conduct the task to guarantee the fuses are maintained correctly.
Before you go, you may want to read these articles:

